In this tool weekly, we focus on carbide tool coating knowledge. Welcome to browse coating tools of our company.
Type of coating
Titanium nitride (TiCN)
The hardness of the coating is higher than that of TiN coating. Due to the increase of carbon content, the hardness of TiCN coating is increased by 33%, and its hardness range is about hv3000-4000 (depending on the manufacturer).
CVD diamond coating
Compared with PVD coated tools, the life of CVD diamond coated tools is increased 10-20 times. The high hardness of diamond coated tools makes the cutTiNg speed 2-3 times higher than that of uncoated tools. The CVD diamond oxidation temperature refers to the temperature value when the coating begins to decompose. The higher the oxidation temperature is, the more favorable it is for cutTiNg at high temperature.
Although the hardness of TiAlN coating at room temperature may be lower than that of TiCN coating, it has been proved that TiAlN coating is much more effective than TiCN coating at high temperature. The reason why TiAlN coating can keep its hardness at high temperature is that it can form a layer of alumina between tool and chip, which can transfer heat from tool to workpiece or chip.

Compared with high-speed steel tools, the cutTiNg speed of cemented carbide tools is usually higher, which makes TiAlN become the preferred coating for cemented carbide tools. The pvdtialn coated stone tools are usually used for cemented carbide drills and end mills as a good choice for cutTiNg non-ferrous and non-metallic materials.
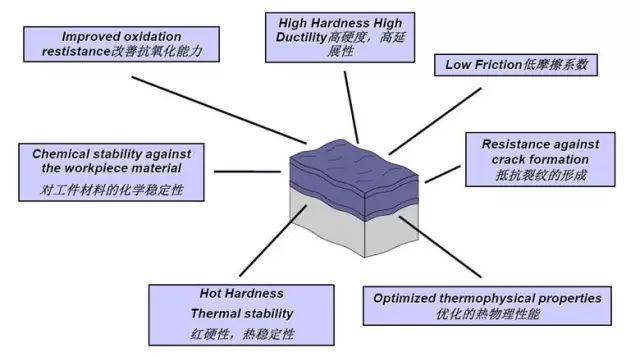
The hard film material on the tool surface has the following requirements
① High hardness and good wear resistance;
② Stable chemical property, no chemical reaction with workpiece material;
③ Heat resistant and oxidation-resistant, low friction coefficient, firm adhesion with matrix, etc. It is difficult for single coating material to meet the above technical requirements.
The development of coating materials has gone through the development stages of tic-a12o3-TiN composite coating, TiCN, TiAlN and other multi-component composite coating from the original single TiN coating and TiC coating. Now, the multi-component composite film materials such as TiN / NbN, TiN / CN, etc. have been newly developed, which greatly improves the performance of tool coating.
The coating material selection criteria
In the manufacturing process of coated cutTiNg tools, it is generally selected according to the hardness, wear resistance, high temperature oxidation resistance, lubricity and adhesion resistance of the coating, among which the oxidation of the coating is the most directly related to the cutTiNg temperature.
Oxidation temperature refers to the temperature value when the coating begins to decompose. The higher the oxidation temperature value is, the more favorable it is for cutTiNg at high temperature. Although the hardness of TiAlN coating at room temperature may be lower than that of TiCN coating, it has been proved that TiAlN coating is much more effective than TiCN coating at high temperature.
The reason why TiAlN coating can keep its hardness at high temperature is that it can form a layer of alumina between tool and chip, which can transfer heat from tool to workpiece or chip. Compared with high-speed steel tools, the cutTiNg speed of cemented carbide tools is usually higher, which makes TiAlN the preferred coating of cemented carbide tools. Cemented carbide bits and end mills usually use this PVD TiAlN coating.
From the perspective of application technology: in addition to cutTiNg temperature, cutTiNg depth, cutTiNg speed and coolant may affect the application effect of tool coating.
Development of common coating materials
TiN is the most mature and widely used hard coating material. At present, the use rate of TiN coated high-speed steel tools in developed countries has accounted for 50% – 70% of high-speed steel tools, and the use rate of some complex tools that can not be reground has exceeded 90%.
Due to the high technical requirements of modern metal cutTiNg tools, TiN coating is increasingly unable to adapt. TiN coating has poor oxidation resistance. When the temperature reaches 500 ℃, the film is obviously oxidized and ablated, and its hardness can not meet the needs. TIC has higher microhardness, so the material has better wear resistance. At the same time, it has a firm adhesion with the substrate. In the preparation of multilayer wear-resistant coating, tic is often used as the underlying film in contact with the substrate. It is a very common coating material in coating tools.

With the development of TiCN and TiAlN, the performance of coated tools has been improved. TiCN can reduce the internal stress of the coating, improve the toughness of the coating, increase the thickness of the coating, prevent the spread of cracks, and reduce the cutTiNg edge collapse. When TiCN is set as the main wear-resistant layer of coated tools, the tool life can be significantly improved.
TiAlN has good chemical stability, oxidation resistance and wear resistance. When processing high alloy steel, stainless steel, qinalloy and nickel alloy, its service life is 3-4 times longer than that of TiN coated tools. If there is a high concentration of Al in TiAlN coating, a thin layer of non-conforming A12O3 will be formed on the coating surface during cutTiNg, forming a hard inert protective film. The coated tool can be more effectively used in high-speed cutTiNg. Titanium nitrogen carbide ticno doped with oxygen has high microhardness and chemical stability, which can produce the same effect as tic deca12o3 composite coating. Wechat for metal processing, good content, worthy of attention.
Among the hard film materials mentioned above, there are three kinds whose microhardness HV can exceed 50gpa: diamond film, CBN and carbon nitride.
Many diamond films are required to be deposited at 600 ℃ – 900 ℃, so this technology is often used to deposit diamond films on the surface of cemented carbide tools. The commercialization of diamond carbide tools is a great achievement of coating technology in recent years.
CBN is second only to diamond in hardness and thermal conductivity. It has excellent thermal stability and does not oxidize when heated to 1000 ℃. CBN has very stable chemical properties for ferrous metals. Unlike diamond, CBN is not suitable for steel processing. It can be widely used in finishing and grinding of steel products.
In addition to its excellent wear resistance, CBN coating can also process heat-resistant steel, titanium alloy and quenched steel at quite high cutTiNg speed. It can also cut hard and cold rolls with high hardness, carbon doped quenched materials and Si Al alloy with very serious tool wear. CVD and PVD are the main methods to synthesize CBN films in low pressure gas phase. CVD includes chemical transport PCVD, hot wire assisted heaTiNg PCVD, ECR-CVD, etc.; PVD includes reactive ion beam plaTiNg, active reactive evaporation, laser assisted deposition, etc. There is still a lot of work to be done in the basic research and application of CBN synthesis technology, including reaction mechanism and film-forming process, plasma diagnosis and mass spectrometry analysis, determination of the best process conditions, development of high-efficiency equipment, etc.
Carbon nitride may have hardness up to or above that of diamond. The success of the synthesis of carbon nitride is an outstanding example of molecular engineering. As a super hard material, carbon nitride is expected to have many other valuable physical and chemical properties, and the study of carbon chloride has become a hot topic in the field of material science in the world.

